As a programmer, I find myself using Git and GitHub often to keep track of my project and to keep working on them from different computers. When you try to push your project on GitHub, you'll see that Git will prompt you for your token now. You will also quickly realize that entering your email address and your token will get annoying. But there is one way to fix this, that way is SSH Keys. In this article, I will first go over how to create an SSH key and after I will explain how to add it to your GitHub account.
What is an SSH Key?
First things first, what is an SSH Key? An SSH key, which stands for Secure Shell key, is a cryptographic key that is used for authenticating and securing SSH connections between a client and a server. SSH is a protocol that provides a secure way to access and manage a remote server over an unsecured network. SSH keys provide a more secure and convenient method of authentication compared to traditional password-based authentication.
Usually, SSH keys come in pairs: a private key and a public key. The private key is kept secret and stored securely on your machine. It should never be shared or exposed!
The public key is meant to be shared freely and is placed on the remote server (GitHub) in a special file called authorized_keys.
But how does the keys work? Basically, when you try to connect to a server, it will generate a challenge that can only be decrypted by your private key, which corresponds to your public key stored on the server. Then your computer uses the private key to decrypt the challenge and sends the decrypted information back to the server. Finally, the server verifies the decrypted information. If it matches, then you are authenticated and granted access!
Generating your SSH Key
Generating an SSH Key is actually quite simple and really only takes one command but that command can use different algorithm:
- rsa (the one we will go over in this article)
- dsa
- ecdsa
- ed25519
Like mentioned in the list, we will focus on the rsa key generation for now. The rsa is an algorithm based on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. When using the rsa, you need to specify a size in bits for your key. The minimum is 2048, but nowadays, people usually use 4096 bits.
In order to generate your keys, you will need to open your terminal (or command prompt) and use this command:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
From there, follow the prompts and give your keys a name and a password if you feel like it. Don't forget to store safely your keys, especially the private one. If you are using a Unix based system (like *Ubuntu), I recommend keeping your keys in the .ssh directory of your computer.
Congratulations, you generated your SSH keys. From there, you can use the following command to add your user id to a server if you feel like it:
ssh-copy-id user@remote_server
Where
Connecting your new SSH Key to your GitHub account
Now that you have your SSH key generated, let's add it to your GitHub account. To do so, first open GitHub and head over to the settings page. on the side bar on the left, you should be able to see a section called SSH and GPG keys. Clicking on it should open the page about SSH and GPG keys
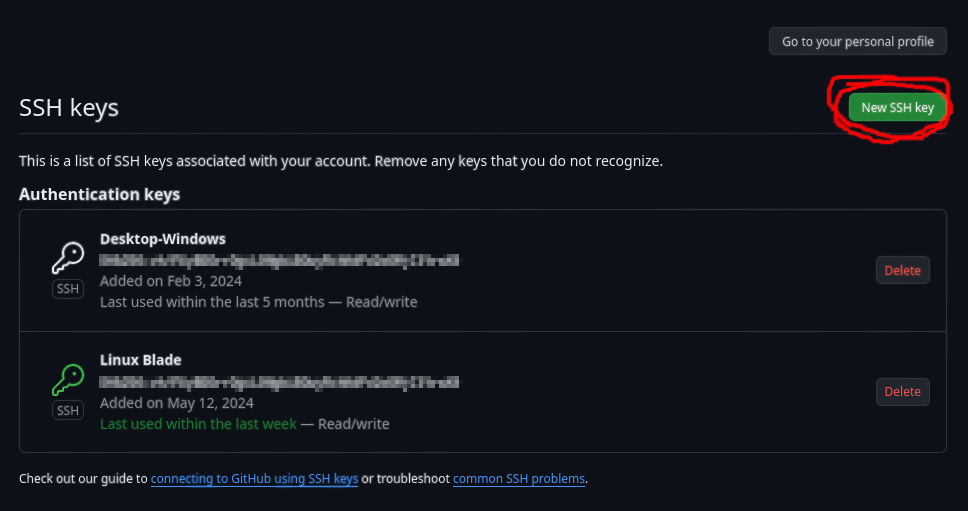
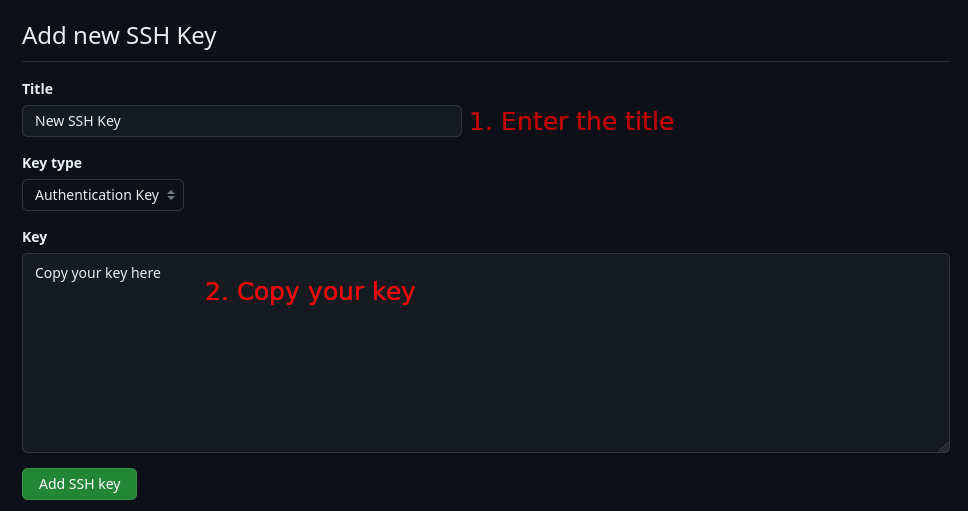
From there, nothing easier, click on the New SSH key button to add your key. Once on that page, give your SSH key a title and copy your public key (the file ending in .pub) in the key text area. Once you copied it, click on the Add SSH key button, and you are done!
From now on, you can use the SSH cloning instead of the HTML, which will use your SSH key instead to authentify your connection. But do keep in mind that your key is only good for the computer you generated it with, you will have to make another key for any other devices you use.
But why would you use an SSH Key?
An SSH key is, in my opinion, one of the most useful tool to a modern day developer. On top of saving you time and simplifying your connection to servers by connecting you automatically to them, it also enhances the security of your connection. I also think that SSH keys are one of the easiest terminal based tools to learn and start practicing using terminals. Finally, I think that it's important for every programmer to learn about SSH keys and how to use them, for all of the reasons mentioned above but also because they are getting more and more essential to keep using your usual services like GitHub since they now require tokens and 2FA's, which you can skip using SSH keys.